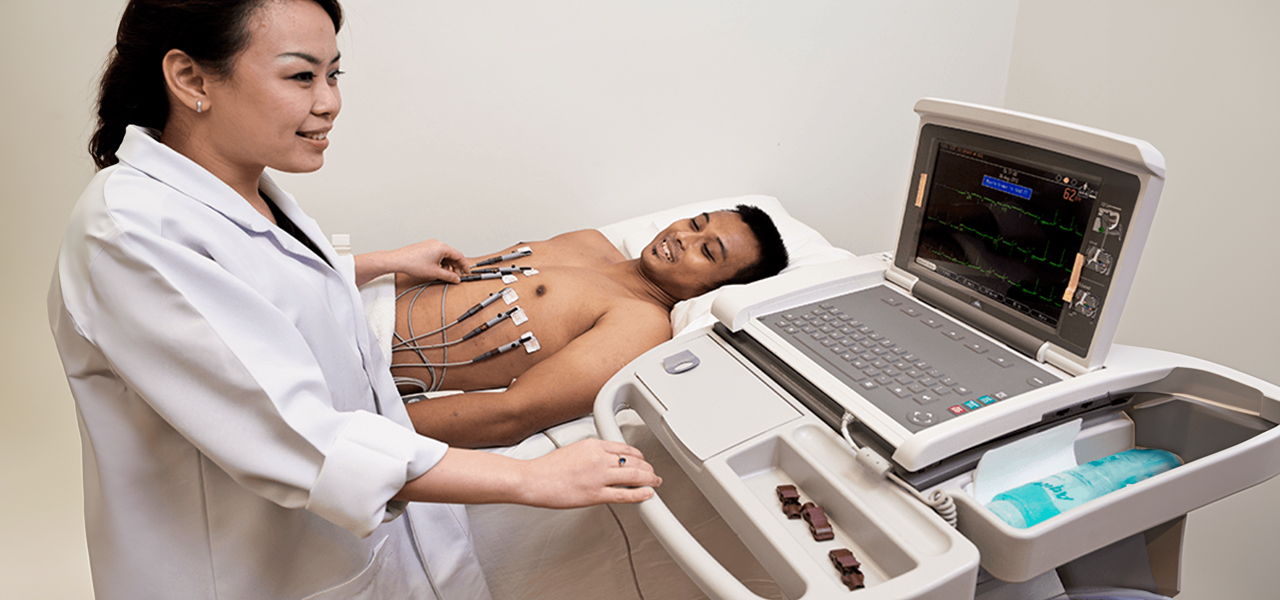
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a diagnostic procedure that measures and probes for any complications or abnormalities with the electrical activity of the heart. An ECG translates the heart’s electrical activity into line tracings that doctors can use to detect abnormal heart rates and rhythms.
An electrocardiogram can be used to:
- Check the heart’s electrical activity
- Understand the cause of chest pains that may be the effect of heart attacks, inflammation of the heart sac, or anginas
- Find the cause of symptoms of heart disease
- Find out the thickness of the heart chambers
- Assess the effectiveness of medication or the presence of side effects
- Monitor the effectiveness of mechanical devices implanted in the heart
- Examine the health of the heart when other diseases or conditions exist (such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes or genetic heart disease)
An ECG is usually ordered to determine if a person is suffering from heart disease. The doctor may recommend an ECG if:
- Patient has chest pains or palpitations
- Surgery is scheduled
- There is a strong family history of heart complications
Services & Procedures Offered
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is conducted by a trained health professional, and the doctor will assess its results.
Before the test, the doctor will talk to patient regarding any medication patient is taking as the doctor may have instructions on how to take them prior to the examination. During the test, patient should not be wearing any jewelry or stockings; men will usually be bare-chested, while women may wear a bra, T-shirt, or gown.
During the procedure, several electrodes will be attached to the skin on each arm and leg, as well as the chest after the areas have been cleaned. The electrodes will then measure the heart’s electrical activity. Patient will be advised to lie still, and breathe normally, or perhaps asked to hold breath. As no actual electricity passes through the body during this procedure, an ECG is harmless and painless.
After the ECG, the doctor will discuss the results with patient. Abnormal results may have a variety of meanings, including:
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Damage or changes to heart muscle
- Changes of blood’s sodium and potassium leeks
- Congenital heart defect
- Enlargement of the heart
- Fluid or swelling in the heart’s surrounding sac
- Inflammation of the heart (myocarditis)
- A past of current heart attack
- Poor blood supply to arteries
Besides the standard ECG (sometimes called a resting ECG) described above, there are also other types of ECG:
- Exercise ECG taken while patient is exercising to show how the heart copes under stress
- 24- or 48- hour ECG where patient will be required to wear an electronic recorder for 24/48 hours (also called a Holter monitor or ambulatory ECG)
- Cardiac event recorder that records patient’s heartbeat over a longer period of time






