Medication Information & Its Administration Technique
Moisturizers vs Steroids
Eczema is a skin condition caused by inflammation of the skin. Eczema causes skin to become itchy, red, dry; and sometimes even cracked and leathery.
Moisturizers
- Helps prevent further water loss
- Main role is to prevent eczema from flaring up
- The difference between lotions, creams and ointments is the proportion of oil (lipid) to water
- The higher the lipid content, the thicker the emollient. Hence, the better and longer it works.
- The type to use depends on the dryness of your skin, the area of skin involved and your preference:
- Mild skin dryness – Lotion or Cream
- Moderate skin dryness – Cream or Ointment
- Areas of hairy skin – Lotion
Topical Steroids
Topical steroids work by reducing inflammation of the skin and clearing flare-ups.
How to apply moisturizers?
- Use moisturizers at least twice a day, after a shower and before bedtime.
- They are best applied within 3 minutes after a shower or bath to maximise their moisture-retaining effect.
- Apply moisturizers generously to entire body. This prevents the eczema from developing elsewhere.
How to apply steroid creams?
- Gently rub the cream or ointment into the skin until it disappears. Then wash your hands (unless your hands are the treated area).
- Overuse of steroids can lead to thinning and discolouration of skin.
References: Eczema: How to use Mositurisers and Topical Steroids
Rectal Medications
Types of rectal medications

Rectal Suppositories
Solid, torpedo-shaped pellets that melt at body temperature when inserted into the rectum.

Enemas
Substances in liquid form designed for rectal administration.
Pessaries
Solid, mainly ovoid-shaped preparation for insertion into the vagina (may come with an applicator).
Method of administration of rectal medications
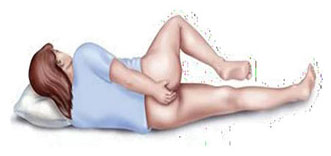
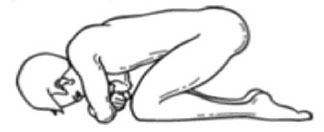
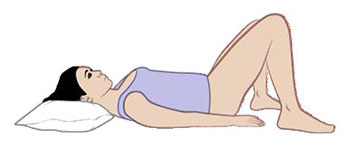
i. Lying position for insertion of rectal suppository or enema.
ii. Prior to insertion

Wash hands and the area of administration with a gentle cleanser/soap and water. Dry it thoroughly.
iii. Proper technique of insertion
Gently push the suppository into the rectum.
Hold buttocks together for a few seconds.
Remain lying down for 5 minutes.
Gently insert the pessary into the vagina, as far as comfortably possible.
If using an applicator, push the plunger until it stops.
Use a sanitary pad to prevent staining.
Insert the tip of the enema into the rectum.
Squeeze the enema to empty all its contents.
Squeeze the buttocks for 2 to 5 minutes.
Safe use of insulin
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows your body to use sugar (glucose) from carbohydrates in the food that you eat for energy or to store glucose for future use. Insulin helps keeps your blood sugar level from getting too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia).

Are You Using Your Insulin in the Correct Way?
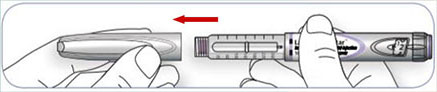
1. Get ready: Remove the pen cap from your insulin pen with clean hands.
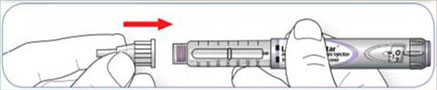
2. Attach the needle: Remove the protective seal and screw the needle on.
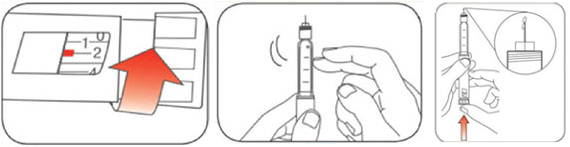
3. Prime before use: Dial the knob to "2" units and gently tap pen to remove air bubbles.
*While holding pen with needle upwards, push the knob until it reaches "0" unit. You should be able to see insulin at the tip of the needle.
4. Select the dose: Dial the knob to the required units prescribed.
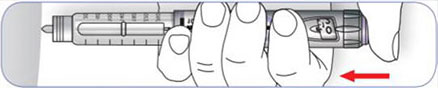
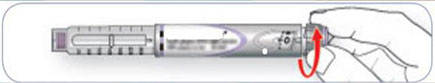
5. Inject your dose: Clean site with alcohol swab, insert needle into skin and press down dial slowly.
*Count to 10 before removing.
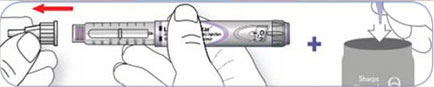
6. Remove the needle: Put outer needle cap back, unscrew and discard used needle.
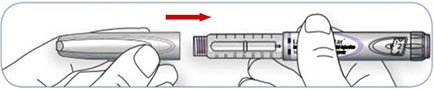
7. Recap insulin pen and store in a safe place at room temperature.
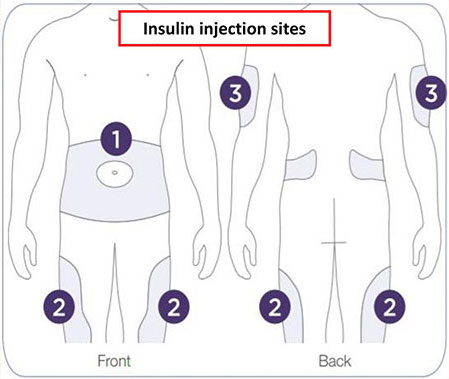
Insulin Injection Sites
Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar):

Dizziness / Headache
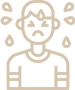
Sweating / Clammy

Blurred Vision

Fast Heartbeat

Hunger
What should you do?
- Check your blood sugar level
- Consume sugar containing beverages e.g. half a glass of fruit juice or 3 teaspoons of white sugar
Inhaler
What type of medication is in your inhaler?
Your inhalers may contain various medications. However, they can generally be classified as reliever and controller/ preventer.

- Provides fast relief of shortness of breath
- Works by opening up the airways quickly (within 3-5 minutes)
- Also recommended to be used by asthmatic patients prior to physical activity
- Does not prevent future occurrences of breathlessness
- Used to prevent / reduce risk of worsening of condition
- Works either by reducing inflammation in the lungs or opening the airways over long periods of time
- Needs to be used consistently to be effective
- May consist of steroid or long acting bronchodilator
- These are inhalers that contain two active ingredients that usually combine a controller with a reliever OR 2 controllers
- This can help to improve adherence to treatment and reduce confusion as there are less inhaler devices to be used
Did you know?
At least 50% of adults and children do not take their controller medications as prescribed. This often leads to poorly-controlled respiratory conditions.If you use a controller and do not feel any improvement after use, know that this is normal because they take time to work. In fact, it is important to comply with the prescribed treatment duration for it to work properly!

References:
GINA pocket guide for asthma management and prevention for adults and children older than 5 years (updated April 2021) Inhalation Drug Delivery Devices –Therapeutic Guideline Australia Inhaler Devices , Health Navigator New Zealand
Different inhalers employ different delivery systems and suit a different group of patients. Choosing the correct system requires consideration of a few factors such as age, developmental stage, inspiratory effect, cognition and dexterity.
Pressurised metered-dose inhalers (pMDI) |
Dry powder inhalers |
Soft mist inhalers |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Method |
Stores medication in a canister and is released under high pressure via the mouthpiece when the inhaler is pressed |
The device is activated by your breath |
No propellant is used in this device. |
Technique required for optimal administration |
This inhaler requires good hand - mouth coordination |
Need to be able to breathe in quickly and deeply or else part of the dose will not be emitted from the inhaler or the particles may be too big to enter your lungs |
This inhaler still requires hand-mouth coordination however is it much easier to operate this device as the medication is emitted much slower compared to pMDI |
Possible disadvantages |
This inhaler may not be suitable for certain groups of people e.g. very young children without the use of spacer, elderly with poor dexterity. |
This inhaler may not be suitable for people who are very short of breath (for example, because of an asthma attack or a flare-up (exacerbation) of COPD. |
Still requires a certain extent of hand-mouth coordination |
Examples |
 |
 |
 |
References: Images credit to The Lung Association, Saskatchewan, Canada.
How to Use Your Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI)?
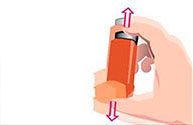
Shake the device by holding it upright with your thumb on the base below the mouthpiece.
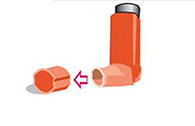
Remove the mouth piece cover.
*If you are using steroid-containing inhalers, remember to gargle your mouth after using the inhaler. Do not swallow the water.

Breathe out as much as you can, away from the device.
*Repeat the steps after 30 seconds to 1 minute if second dose is required.
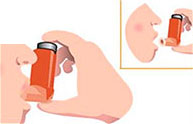
Close your mouth around the mouthpiece to form a tight seal. Do not bite the mouthpiece.
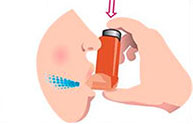
Breathe in slowly through your mouth. As you do this, press down the top of the canister to release a puff while still breathing in steadily and deeply.
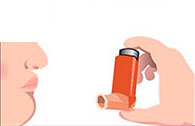
Hold your breath for at least 10 seconds. While doing so, you can remove the device from your mouth.
Using your MDI with a spacer device

Remove the cap. Check for any foreign object.

Insert MDI mouthpiece into the back of the chamber.

Place the mask onto the mouthpiece end of the spacer.

Shake the chamber and inhale 4 to 5 times.

Press and hold the mask over the mouth and nose. Spray one puff of medicine into the spacer. Breathe in and out for 6 breaths. Repeat this step if a second dose is required.





